Full form of QR codes is Quick Response codes. QR codes were invented in 1994, by the DENSO Corporation. I’m sure you’ve seen lots of them. They are the natural progression of bar codes. Bar codes are one dimensional, encoding data in a series of alternating high contrast lines. QR codes store data in two dimensions in the form of an array of contrasting regions. The information density of a QR is much higher than a barcode; depending on the format used and the resolution of reader, over a thousand bytes can be encoded in a region the size of a postage stamp.
Table of Contents
What is a QR code?
It’s a QR code is a type of barcode. By scanning it, you access the information encoded in it. In standard barcodes, information is encoded in the width of and distance between vertical lines. In QR , information is encoded in the arrangement of squares. Either way, data transforms into a machine-readable arrangement of visual elements. And upon scanning by an optical scanning device, the data translates back to its original form.But three things make QR extra special. The amount of data they can hold, how quickly they are read, and that virtually all of our phones can instantly and easily scan them. Here’s how these little miracles work.
How Do QR Work?
A QR code is a scan able barcode encoded with data. Encoded means converted into a particular form. In the case of QR, numeric and alphanumeric characters, bytes, and kanji convert into a unique two-dimensional arrangement of squares. When an optical scanner passes over those squares, it translates their arrangement back into that data’s original form.In the QR , the arrangement of the squares—or data modules, as they’re called—is actually URL. It’s just been translated from the alphanumeric string of the URL into a collection of squares. That’s how you go from link to QR code. A QR scanner will then translate it back to the original URL.
The anatomy of a QR Code
The parts of a QR code is mostly relevant to anyone thinking of creating a QR . Be aware, though, of the QR security risks associated with free online services.
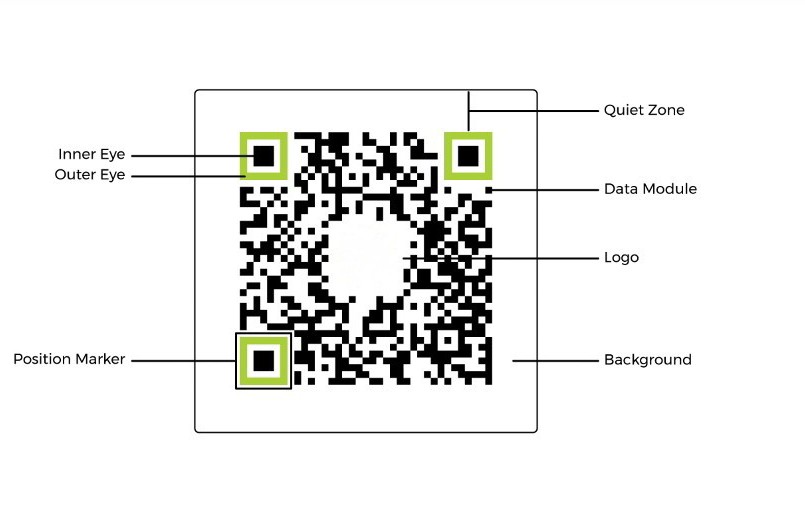
The most important parts of a QR code are:
- Data module: This is the standard unit of the QR . It’s typically a black square set against a white background. Though the colors and contrast can be different, black-on-white is the most optimal when creating a custom QR . The arrangement of these black squares, or data modules, is what makes up the majority of a QR .
- Position marker: There are three position markers on every QR . Consisting of an inner and outer eye, they allow scanners and cameras to quickly and accurately locate the data modules and the scanning direction.
- Quiet zone: This is the blank area on all sides of the data module matrix that contains all the data modules and position markers. It allows scanners and readers to optically place where the QR begins and ends.
What Information Is in a QR Code?
There are three types of information that a QR stores: size, error correction level, and data type.
Size of QR Code
- A QR code can be made up of a maximum of 177 rows and 177 columns, which makes for a possible 31,329 data modules. Most QR aren’t that big, though.The size of a QR corresponds to its version. The smallest a QR can be is 21 rows by 21 columns, which is version 1. 25×25 is version 2, and on and on. The aforementioned largest QR possible, 177×177, is version 40.
Error Correction Levels:
- Encoded in a QR code is one of four QR code error correction levels. The higher the correction level, the more damage a QR can sustain while still being scannable. It’s like a stored backup of the QR code. The lower the correction level, the more space left for size and data.
Data Type
- QR codes can store up to 7,089 numeric characters or 2,953 alphanumeric characters. They can also store bytes and kanji, but those are less frequently used. These numbers assume the lowest error correction level.
QR can store a variety of information, including numbers, letters, punctuation, and symbols, making them versatile for uses like business cards, restaurant tables, authentication, hotel check-ins, website logins, contactless payments, and digital wine lists. Unlike standard one-dimensional barcodes, which hold about 20 to 100 characters, QR can handle much larger amounts of data. While storing more characters does complicate the QR’s design, this isn’t always the case, as there’s a distinction between static and dynamic QR.
How Do QR Code Work Technically?
While learning how to scan a QR code is easy for you, the QR and scanner are doing a bit more work.The QR scanner begins at the bottom right of the QR . It then moves up two data modules at a time until it hits the first position marker. Then it moves two data modules to the left and goes down. It repeats this right-to-left, up-then-down zig-zag process until every data module is covered.Here’s a basic six-step outline of how the scanning process works.
Here’s a basic six-step outline of how the scanning process works.
- Point your phone at a QR code.
- The QR scanner in your phone’s camera recognizes the three position markers in the QR code. With a sufficient quiet area, your scanner is now aware of where the edges of the QR are.
- The scanner begins at the bottom right, where it encounters the mode indicator. These four data modules indicate what data type (numeric, alphanumeric, byte, or kanji) the rest of the encoded data is.
- Next, the scanner encounters the character count indicator, which are the next 8 data modules up from the mode indicator. These indicate how many characters the total encoded data is.
- Knowing the data type and character length, the scanner then continues its zig-zag path along the data modules until all it retrieves all the encoded information and reaches the end indicator.
- After reading the final character, the scanner proceeds along its path to the error correction data modules. Within these encoded modules are one of four levels of error correction. Or how much of the QR’s encoded data is backed up in case of code damage.
This should help you visualize how a QR works:
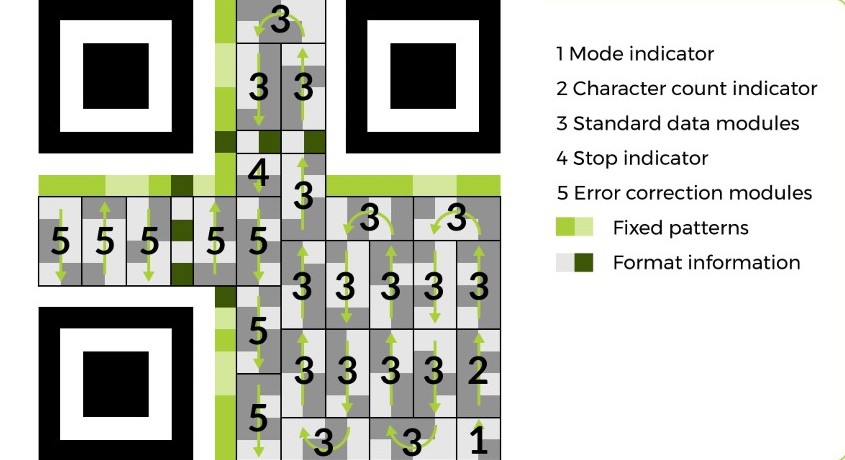
and that’s how QR code work!
follow for more our social account.



One Comment